
This clause introduces the main concepts of the CC. It identifies the target audience, evaluation context, and the approach taken to present the material.
Information held by IT products or systems is a critical resource that enables organisations to succeed in their mission. Additionally, individuals have a reasonable expectation that their personal information contained in IT products or systems remain private, be available to them as needed, and not be subject to unauthorised modification. IT products or systems should perform their functions while exercising proper control of the information to ensure it is protected against hazards such as unwanted or unwarranted dissemination, alteration, or loss. The term IT security is used to cover prevention and mitigation of these and similar hazards.
Many consumers of IT lack the knowledge, expertise or resources necessary to judge whether their confidence in the security of their IT products or systems is appropriate, and they may not wish to rely solely on the assertions of the developers. Consumers may therefore choose to increase their confidence in the security measures of an IT product or system by ordering an analysis of its security (i.e. a security evaluation).
The CC can be used to select the appropriate IT security measures and it contains criteria for evaluation of security requirements.
There are three groups with a general interest in evaluation of the security properties of IT products and systems: TOE consumers, TOE developers, and TOE evaluators. The criteria presented in this document have been structured to support the needs of all three groups. They are all considered to be the principal users of this CC. The three groups can benefit from the criteria as explained in the following paragraphs.
The CC plays an important role in supporting techniques for consumer selection of IT security requirements to express their organisational needs. The CC is written to ensure that evaluation fulfils the needs of the consumers as this is the fundamental purpose and justification for the evaluation process.
Consumers can use the results of evaluations to help decide whether an evaluated product or system fulfils their security needs. These security needs are typically identified as a result of both risk analysis and policy direction. Consumers can also use the evaluation results to compare different products or systems. Presentation of the assurance requirements within a hierarchy supports this need.
The CC gives consumers - especially in consumer groups and communities of interest - an implementation-independent structure termed the Protection Profile (PP) in which to express their special requirements for IT security measures in a TOE.
The CC is intended to support developers in preparing for and assisting in the evaluation of their products or systems and in identifying security requirements to be satisfied by each of their products or systems. It is also quite possible that an associated evaluation methodology, potentially accompanied by a mutual recognition agreement for evaluation results, would further permit the CC to support someone, other than the TOE developer, in preparing for and assisting in the evaluation of a developer's TOE.
The CC constructs can then be used to make claims that the TOE conforms to its identified requirements by means of specified security functions and assurances to be evaluated. Each TOE's requirements are contained in an implementation-dependent construct termed the Security Target (ST). One or more PPs may provide the requirements of a broad consumer base.
The CC describes security functions that a developer could include in the TOE. The CC can be used to determine the responsibilities and actions to support evidence that is necessary to support the evaluation of the TOE. It also defines the content and presentation of that evidence.
The CC contains criteria to be used by evaluators when forming judgements about the conformance of TOEs to their security requirements. The CC describes the set of general actions the evaluator is to carry out and the security functions on which to perform these actions. Note that the CC does not specify procedures to be followed in carrying out those actions.
While the CC is oriented towards specification and evaluation of the IT security properties of TOEs, it may also be useful as reference material to all parties with an interest in or responsibility for IT security. Some of the additional interest groups that can benefit from information contained in the CC are:
a) system custodians and system security officers responsible for determining and meeting organisational IT security policies and requirements;
b) auditors, both internal and external, responsible for assessing the adequacy of the security of a system;
c) security architects and designers responsible for the specification of the security content of IT systems and products;
d) accreditors responsible for accepting an IT system for use within a particular environment;
e) sponsors of evaluation responsible for requesting and supporting an evaluation; and
f) evaluation authorities responsible for the management and oversight of IT security evaluation programmes.
In order to achieve greater comparability between evaluation results, evaluations should be performed within the framework of an authoritative evaluation scheme that sets the standards, monitors the quality of the evaluations and administers the regulations to which the evaluation facilities and evaluators must conform.
The CC does not state requirements for the regulatory framework. However, consistency between the regulatory frameworks of different evaluation authorities will be necessary to achieve the goal of mutual recognition of the results of such evaluations. Figure 3.1 depicts the major elements that form the context for evaluations. depicts the major elements that form the context for evaluations.
Use of a common evaluation methodology contributes to the repeatability and objectivity of the results but is not by itself sufficient. Many of the evaluation criteria require the application of expert judgement and background knowledge for which consistency is more difficult to achieve. In order to enhance the consistency of the evaluation findings, the final evaluation results could be submitted to a certification process. The certification process is the independent inspection of the results of the evaluation leading to the production of the final certificate or approval. The certificate is normally publicly available. It is noted that the certification process is a means of gaining greater consistency in the application of IT security criteria.
The evaluation scheme, methodology, and certification processes are the responsibility of the evaluation authorities that run evaluation schemes and are outside the scope of the CC.
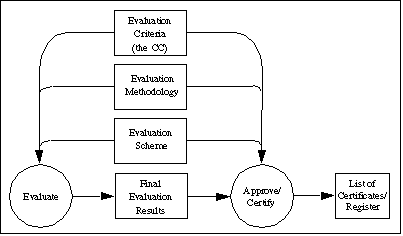
Figure 3.1 - Evaluation context
The CC is presented as a set of distinct but related parts as identified below. Terms used in the description of the parts are explained in clause 4.
a) Part 1, Introduction and general model, is the introduction to the CC. It defines general concepts and principles of IT security evaluation and presents a general model of evaluation. Part 1 also presents constructs for expressing IT security objectives, for selecting and defining IT security requirements, and for writing high-level specifications for products and systems. In addition, the usefulness of each part of the CC is described in terms of each of the target audiences.
b) Part 2, Security functional requirements, establishes a set of functional components as a standard way of expressing the functional requirements for TOEs. Part 2 catalogues the set of functional components, families, and classes.
c) Part 3, Security assurance requirements, establishes a set of assurance components as a standard way of expressing the assurance requirements for TOEs. Part 3 catalogues the set of assurance components, families and classes. Part 3 also defines evaluation criteria for PPs and STs and presents evaluation assurance levels that define the predefined CC scale for rating assurance for TOEs, which is called the Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs).
In support of the three parts of the CC listed above, it is anticipated that other types of documents will be published, including technical rationale material and guidance documents.
The following table presents, for the three key target audience groupings, how the parts of the CC will be of interest.
| Consumers | Developers | Evaluators | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Use for background information and reference purposes. Guidance structure for PPs. | Use for background information and reference for the development of requirements and formulating security specifications for TOEs. | Use for background information and reference purposes. Guidance structure for PPs and STs. |
| Part 2 | Use for guidance and reference when formulating statements of requirements for security functions. | Use for reference when interpreting statements of functional requirements and formulating functional specifications for TOEs. | Use as mandatory statement of evaluation criteria when determining whether a TOE effectively meets claimed security functions. |
| Part 3 | Use for guidance when determining required levels of assurance. | Use for reference when interpreting statements of assurance requirements and determining assurance approaches of TOEs. | Use as mandatory statement of evaluation criteria when determining the assurance of TOEs and when evaluating PPs and STs. |